Implementing Zero Trust Security Framework: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlike the traditional security model that assumes everything within the premises is secure, Zero Trust is an added layer of security. As a new cybersecurity framework, it evolves from traditional legacy perimeter security models to a dynamic granular “Never Trust, Always Verify” model. It implements stringent verification and continuous authentication for all users, devices, network flow, and connection, regardless of location and identity within or outside the network perimeter.
With Zero Trust security framework, the business can recognize the attackers, who can potentially breach the perimeter defenses and gain access to sensitive data or systems. It can also handle a sheer volume of data transactions and counteract sophisticated cyberattacks with unparalleled speed and accuracy.
At its core, Zero Trust encompasses a few fundamental principles
- Verify before trusting: All users and devices, regardless of location, must be authenticated and authorized before being granted access to resources.
- Least privileged access: Users and devices must be granted only the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks. This principle of least privilege (PoLP) helps minimize the attack surface and limit potential damage in a security breach.
- Micro-segmentation: The network is divided into smaller, isolated segments to minimize the impact of a potential breach. Each segment has its security controls and policies.
- Security enforcement: Strict security policies are applied and enforced across the network, regardless of location or device used. This includes security features like Multifactor Authentication (MFA), encryption, and access control mechanisms.
- Continuous monitoring: Monitoring and analyzing user and device behavior are essential to detect anomalous or suspicious activities that may indicate security threats.
Role of Modern Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) in Zero Trust Security
ZTNA is considered the “holy grail” of network security that leverages identity and context-based user identities instead of relying on security parameters for authentication and authorization. Enforcing clearly defined access control mechanisms establishes secure remote access to an organization’s assets, such as applications, data, and services, thus preventing public visibility and significantly reducing the possibility of surface area for attack.
The Key Characteristics of ZTNA
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP features prevent the illicit data transfer of sensitive data outside the organization through incorporating encryption on download or blocking techniques.
- Scalable Performance: ZTNA connects remote workers to business applications, so the solution needs to be flexible and dependable to minimize downtime. Cloud hosting allows businesses to quickly adjust resources based on traffic spikes, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
- Granular visibility and reporting: It provides a comprehensive network view, enabling security audits and demonstrating a commitment to regulatory requirements.
- Bring Your Own Devices (BYOD): BYOD allows employees to use their devices without special software. This saves money on buying new equipment. ZTNA can also be implemented using agent-based alternatives for controlled devices.
- Advanced Threat Protection (ATP): ATP defends the organization's endpoints from cyberattacks, including zero-day attacks, using threat prevention against sophisticated and advanced threat actors.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security Framework
Zero Trust is the most effective security model that provides robust protection against malicious attacks in today’s complex threat landscape.
- Enhanced Data Protection: The primary benefit of applying Zero-Trust security principles is to reduce the attack surfaces of the organization. By implementing micro-segmentation, Zero Trust Security protects organizations from data breaches, leaks, and unauthorized access, enhancing network security at a granular level.
- Invisible infrastructure: ZTNA allows users to access applications without connecting them to the corporate network. It eliminates risk to the network while keeping infrastructure completely invisible.
- Gaining Greater Visibility and Control: The improved visibility of zero trust security helps organizations better understand their network activities, identify potential vulnerabilities, and make more informed decisions by implementing granular controls and access control mechanisms.
Navigating Zero Trust in Cybersecurity: Implementation Roadmap and Best Practices
Zero trust security can be implemented on top of the existing infrastructure without replacing existing technology. It involves adopting security products tailored to function within a zero-trust environment. However, there is a pressing need for a well-planned strategy and roadmap to implement and integrate security tools and technologies to protect our ecosystems against potential cyber threats.
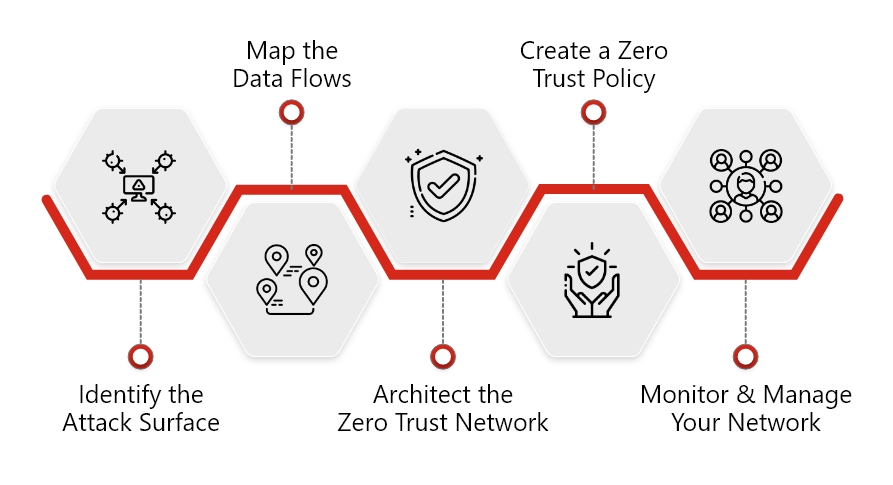
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Security Framework
AI-powered Cybersecurity means a Better User Experience!
Step #1: Identifying Attack Surface
Defining your attack surface is crucial in effectively implementing zero-trust security models. It involves conducting a thorough assessment and understanding of vulnerabilities in various endpoints, such as networks, systems, and applications across organizations, preventing malicious actors from exploiting them.
Step #2: Mapping the Data Flows
Mapping and visualizing the data flow from their source to destination helps organizations identify the security vulnerabilities within the network, leading to the enforcement of security controls to protect information from unauthorized access.
Step #3: Architect the Zero Trust Network
Building a zero-trust network begins with an NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall) to create micro-segmentation of your network. Ensuring the users through implementing Multifactor Authentication (MFA), Least Privileged Access, and conditional access policies before granting access.
Step #4: Create a Zero Trust Policy
Establishing guidelines, measures, and best practices is crucial for deploying a zero-trust framework. Since it ensures that no identity is trusted implicitly, enforcing strict access control mechanisms at every level is paramount.
Step #5: Monitoring Your Network
Effective zero-trust implementation requires robust monitoring and analytics capabilities. Furthermore, incorporating real-time threat intelligence (AI) and incident response mechanisms is pivotal to proactively identifying and addressing emerging threats.
Bottom Line
The paradigm shift from a trust-based to a verification-based security model is not just a fleeting trend; it is imperative for today’s digital landscape. As organizations worldwide rapidly shift towards remote work and cloud computing, Zero Trust emerges as a beacon of hope. iLink is a leading provider of Zero Trust Security Services across its solutions. It emphasizes this metamorphosis, empowering businesses with the necessary tools to safeguard critical assets, modernize security posture, minimize risks, and ensure regulatory compliance, enabling them to make more informed decisions and drive business agility.
Are you ready to embrace Zero Trust Security Framework to secure the future of your business?



